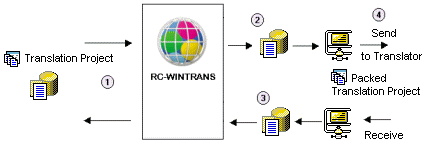
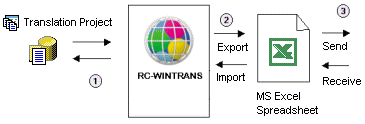
A translation project typically has a number of target languages that are translated by one or more (external) translators. The process by which translators are provided with data to be translated and translators send translated data back for final processing is known as external translation.
RC-WinTrans supports three different ways of exchanging information with translators:
|
1. |
RC-WinTrans: The translator uses RC-WinTrans to translate an RC-WinTrans translation project. |
|
2. |
Microsoft Excel: The translator uses Microsoft Excel to translate Excel Spreadsheets (*.xls) exported from RC-WinTrans. |
|
3. |
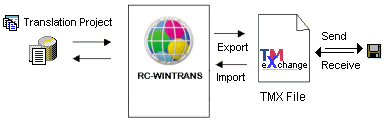
TMX files: The translator uses a translation memory system to translate TMX files exported from RC-WinTrans. |
|
|
Data Exchange Method #1: Translation Project Translated with RC-WinTrans |
|
|
If the translator is in possession of RC-WinTrans, a translation project can be sent to be |
|
translated and then returned upon completion. |
|
You can extract a project for a translator from the main translation project using the Export/Pack a Translation Project command from the File menu.
See also: "Exporting a Translation Project."
After the translator returns the translated project, import it back into the main translation project using the Import | Import from Project commands from the File or Project menus.